

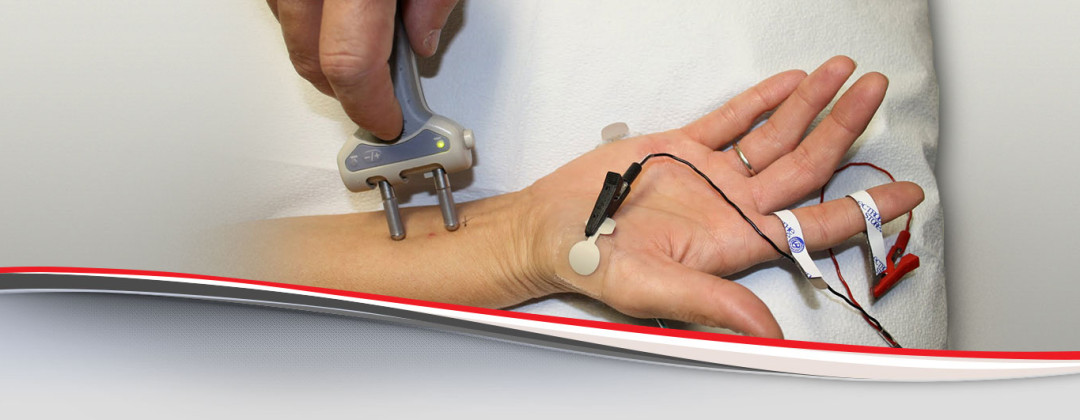
The action potential (size and shape of the wave) that this creates on the oscilloscope provides information about the ability of the muscle to respond when the nerves are stimulated. When an electrode is inserted, a brief period of activity can be seen on the oscilloscope, but after that, no signal should be present.Īfter an electrode has been inserted, you may be asked to contract the muscle, for example, by lifting or bending your leg. Muscle tissue does not normally produce electrical signals during rest. EMG measures the electrical activity of muscle during rest, slight contraction and forceful contraction. An audio-amplifier is used so the activity can be heard. The electrical activity picked up by the electrodes is then displayed on an oscilloscope (a monitor that displays electrical activity in the form of waves). During the test, one or more small needles (also called electrodes) are inserted through the skin into the muscle. The test is used to help detect neuromuscular abnormalities.

Electromyography (EMG) measures muscle response or electrical activity in response to a nerve’s stimulation of the muscle.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
